Figures
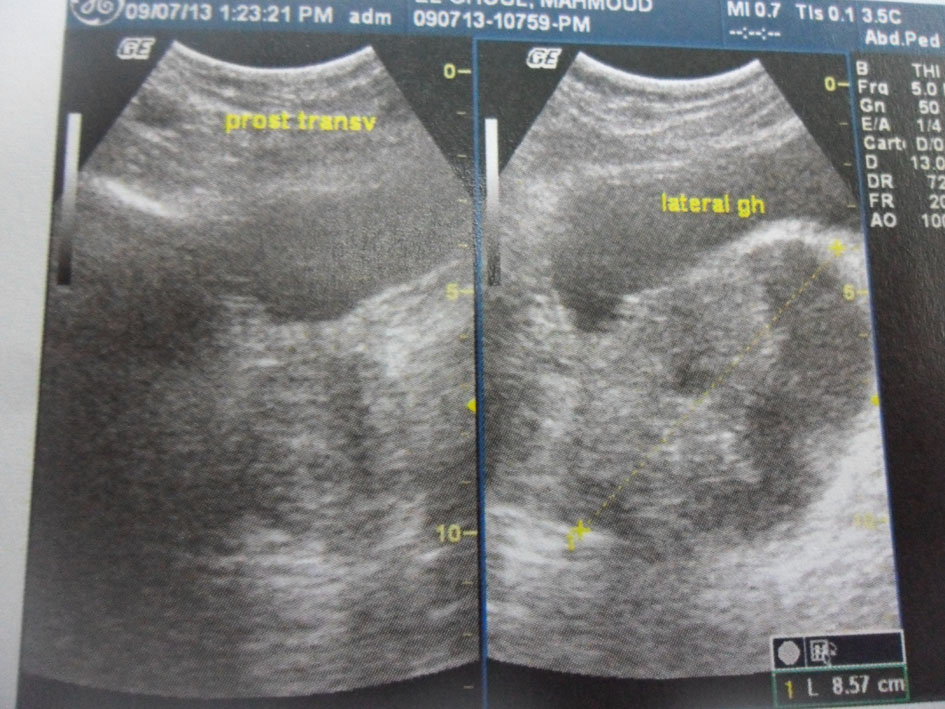
Figure 1. Pelvic ultrasound. An 8.5 cm heterogeneous cystic and solid mass in the left periprostatic region.
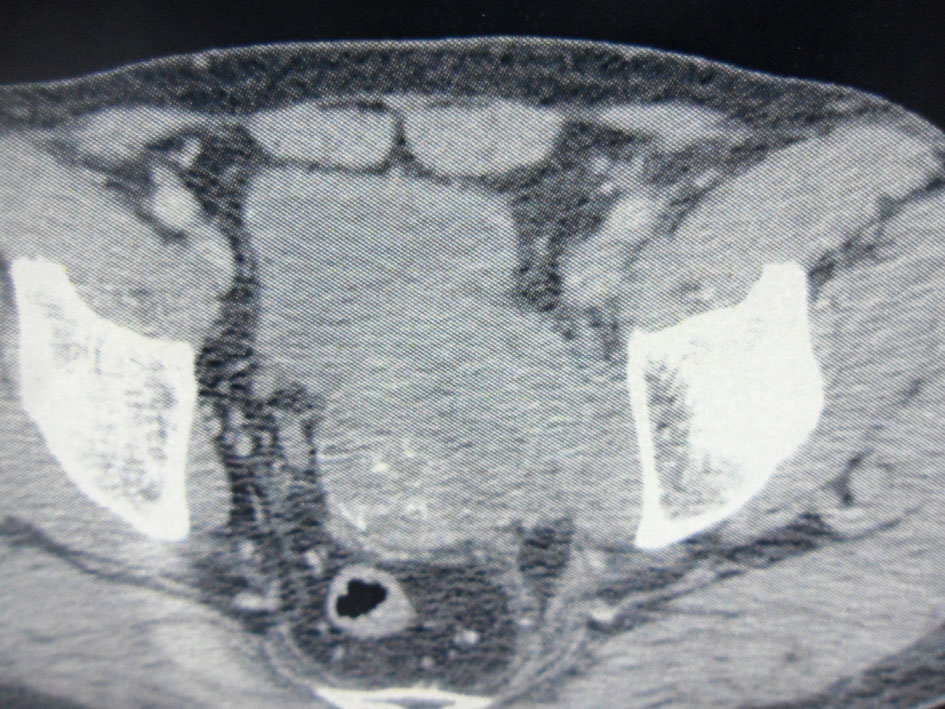
Figure 2. Pelvic computed tomography. An 8.5 × 6 cm solid and heterogeneous mass in the left superior aspect of the prostate with cystic area and peripheral calcifications.
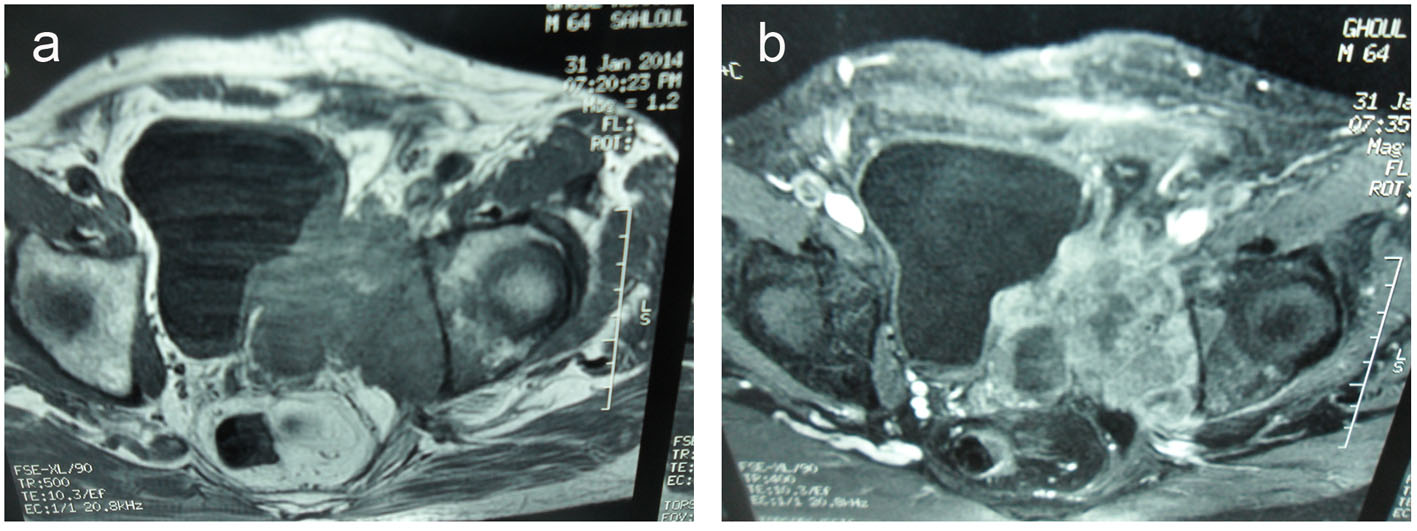
Figure 3. (a) Transverse T2-weighted MR images and transverse T1-weighted MR images (b). A 10 × 9 × 12 cm solid and heterogeneous mass in the left seminal vesicle wall. The mass was hypointense in T1-weighted and hyperintense in T2-weighted MR images compared to the muscle. The mass invades the posterolateral bladder wall, the prostate base, the internal obturator and serratus muscles and the hip bone.
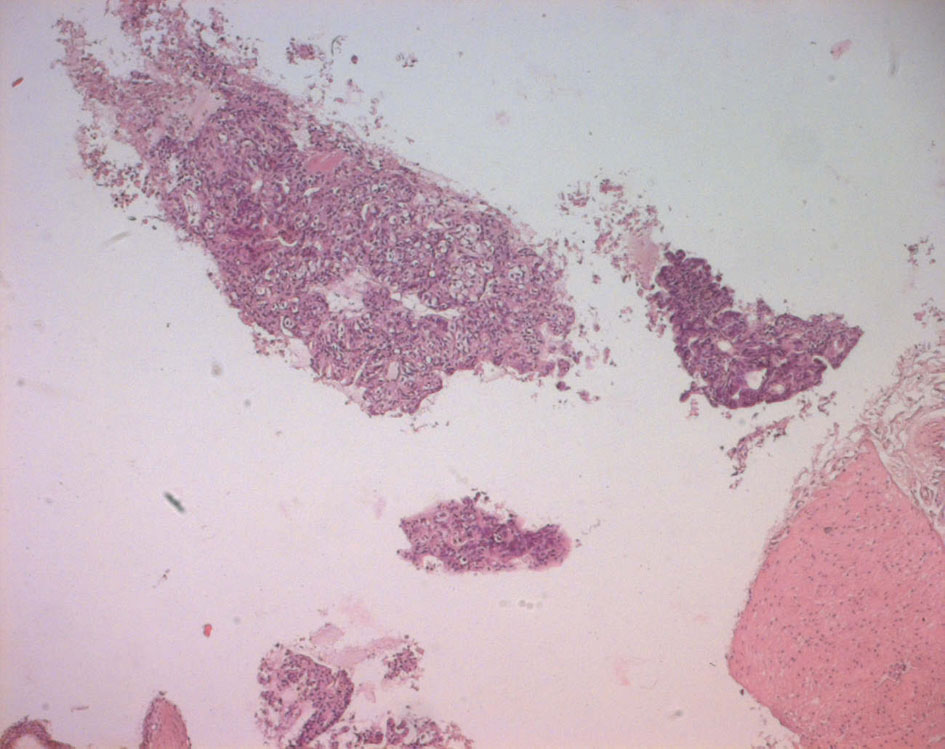
Figure 4. Echo-guided transrectal biopsy (low magnification). Pathological tissue with papillary and pseudo glandular structure, normal prostatic tissue, normal seminal vesicle tissue.
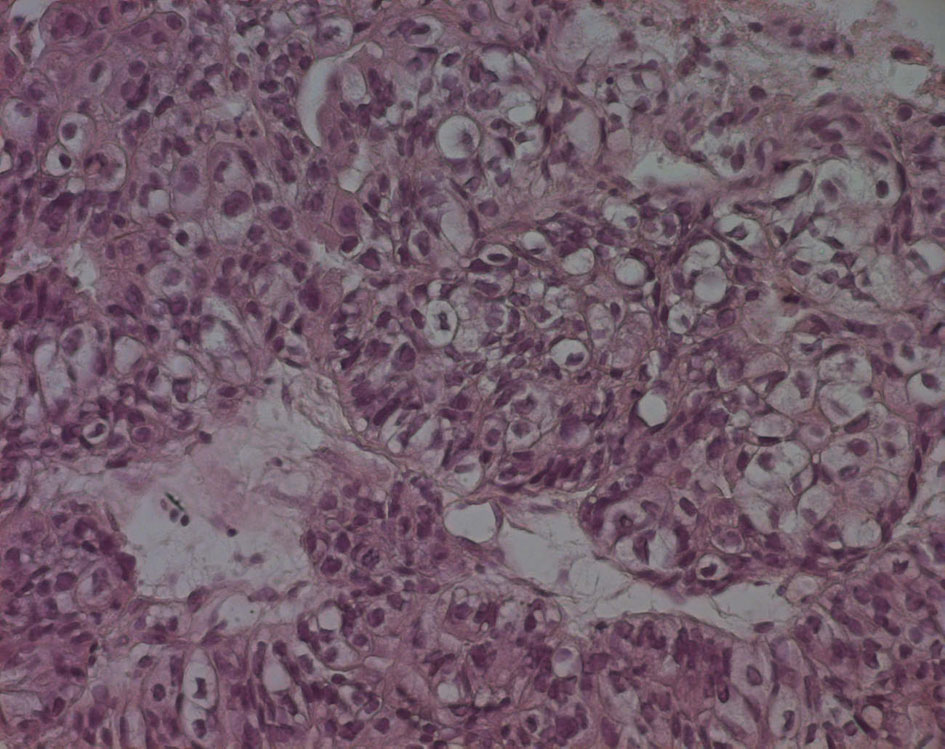
Figure 5. Echo-guided transrectal biopsy (high magnification). Large and medium tumor cells with rounded nucleus and transparent cytoplasm, papillary and glandular structures can be also found.
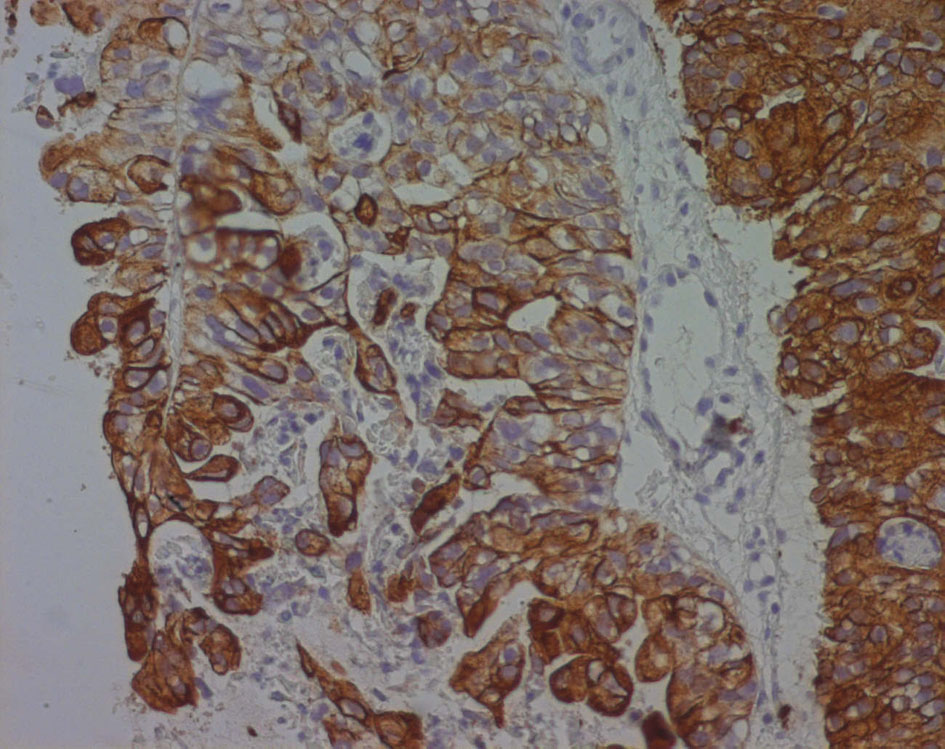
Figure 6. Cytokeratin 7 immunoreactivity in a poorly differentiated seminal vesicle adenocarcinoma. The immunoreactivity appears as a strong brownish cytoplasmic staining in neoplastic cells.
Table
Table 1. Immunohistological Findings in Carcinomas of Seminal Adenocarcinoma and the Most Common Carcinomas in Other Pelvic Organs
| Seminal vesical adenocarcinoma | Prostate carcinoma | Bladder cancer | Rectum cancer | Adenocarcinoma of the Mullerian duct |
|---|
| CA125 | + | - | - | - | ± |
| Cytokeratin 7 | + | ± | ± | - | + |
| PSA | - | + | - | - | - |
| Cytokeratin 20 | - | ± | ± | + | - |
| CEA | ± | - | - | + | ± |






