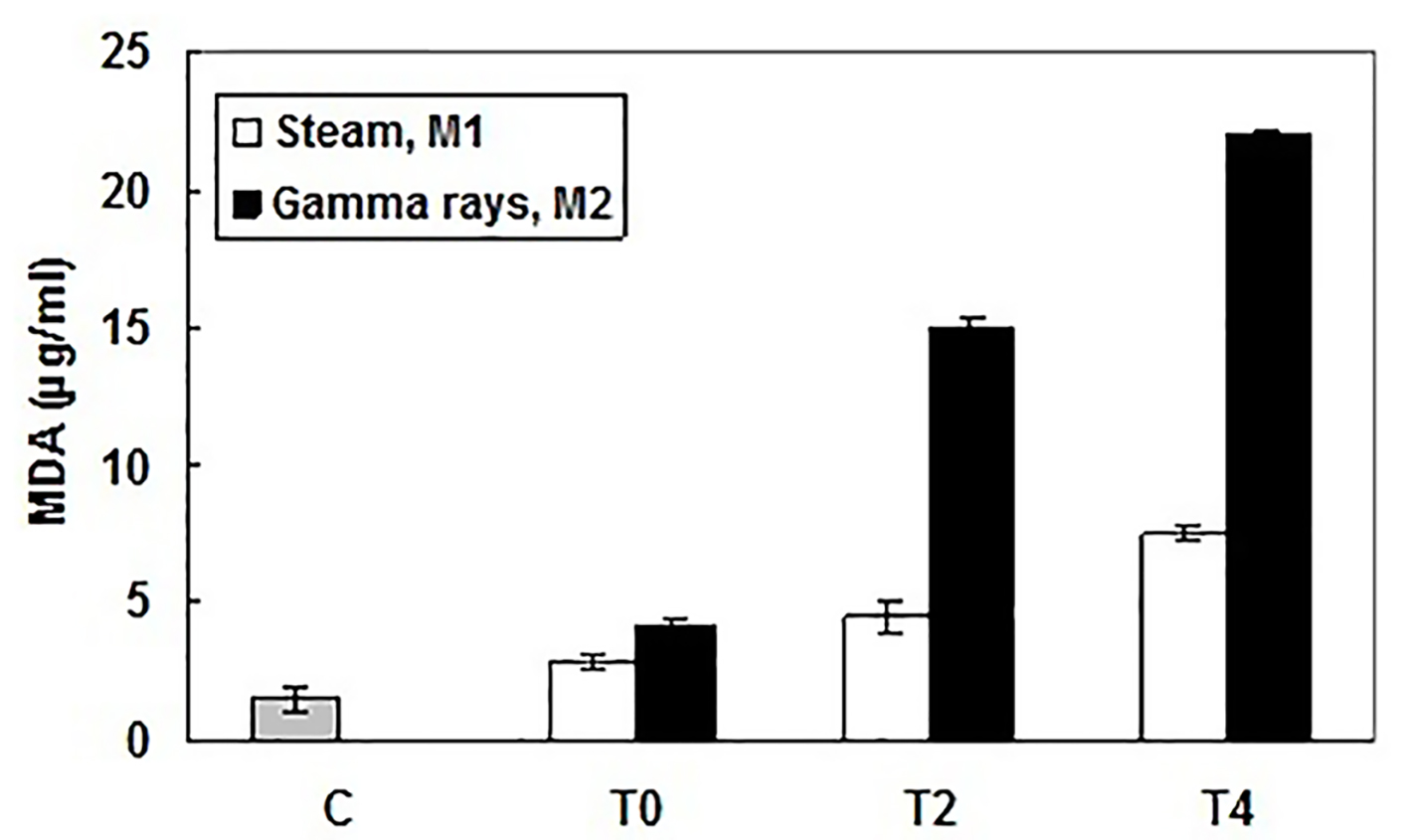
Figure 1. Lipid peroxidation levels in patient and healthy subject sera measured by production of malondialdehyde (MDA), at the beginning (T0), the middle (after 2 h, T2) and the end (after 4 h, T4) of HD session and using different dialyzer sterilization processes: M1 (sterilized by steam) and M2 (sterilized by gamma rays). MDA amounts (µg/mL) were determined according to a standard curve. Results were expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.
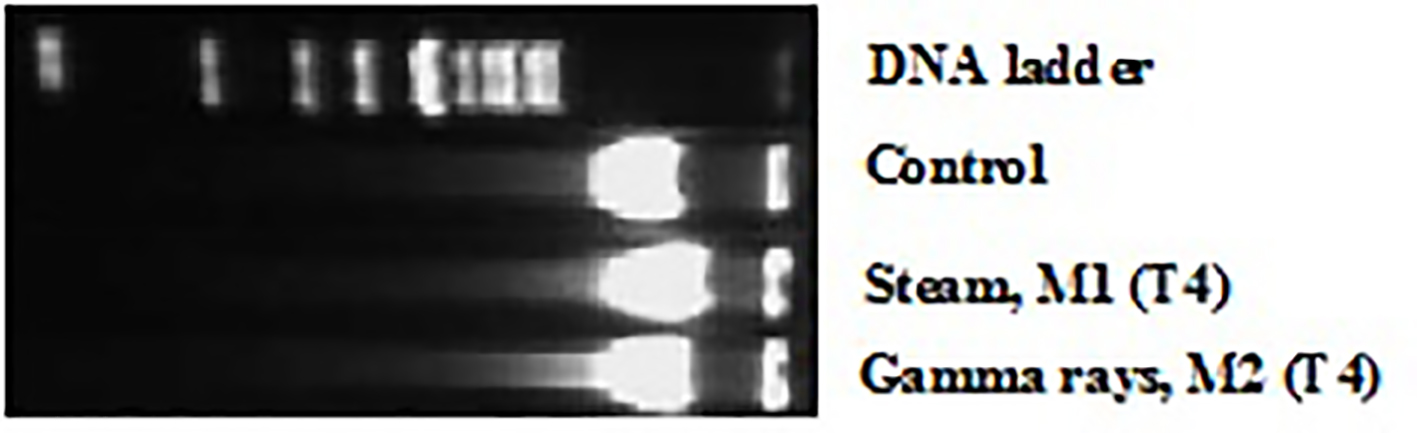
Figure 2. DNA fragmentation induced by exposure to different dialyzer membranes sterilization mode: M1 (sterilized by steam) and M2 (sterilized by gamma rays), in patient leucocytes at the end (after 4 h, T4) of HD session and revealed by agarose gel electrophoresis.
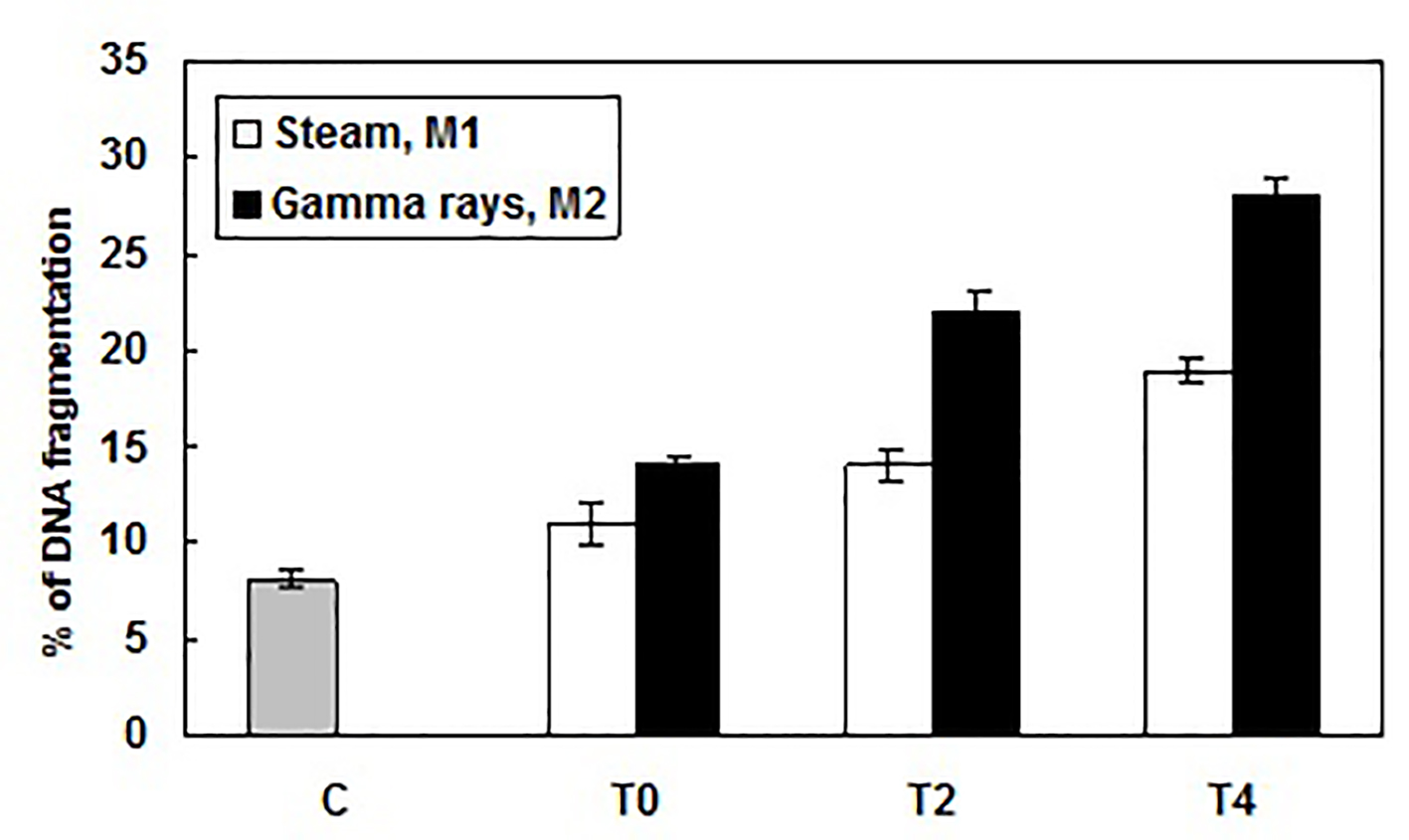
Figure 3. Percentage of DNA fragmentation caused by exposure to different dialyzer membranes sterilization mode: M1 (sterilized by steam) and M2 (sterilized by gamma rays), in patient leucocytes at the beginning (T0), the middle (after 2 h, T2) and the end (after 4 h, T4) of HD session and determined using the diphenylamine assay. Results were expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments.


