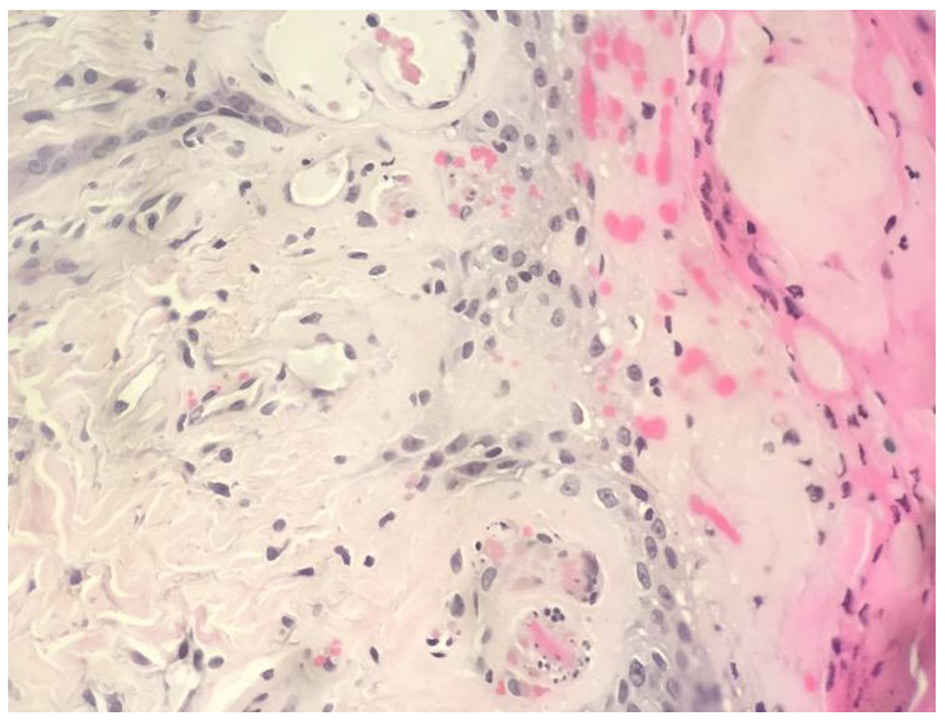
Figure 1. Biopsy findings. The histological section demonstrates fibrin thrombi within small blood vessels and ischemic necrosis of the epidermis, consistent with calcific uremic arteriolopathy (CUA).
| World Journal of Nephrology and Urology, ISSN 1927-1239 print, 1927-1247 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Nephrol Urol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjnu.org |
Case Report
Volume 6, Number 3-4, October 2017, pages 25-28
Calciphylaxis: Early Detection and Off-Label Treatment With Sodium Thiosulfate
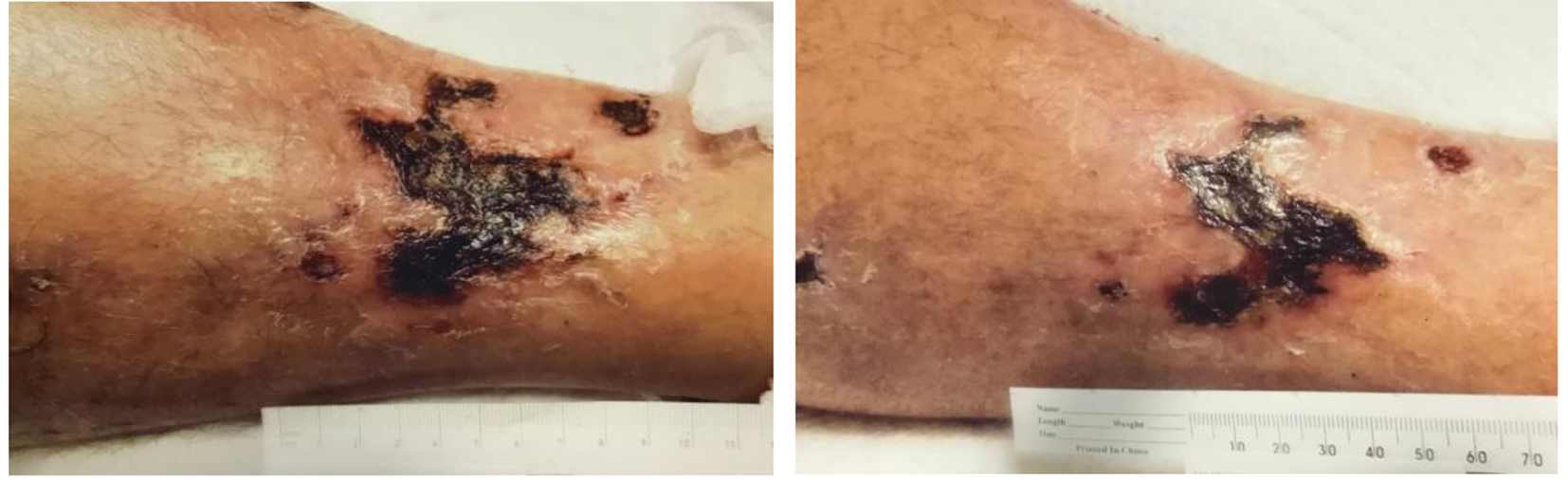
Figures

Tables
| Phosphorus | Albumin | Calcium | Corrected Ca | PTH | Ca × P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.3 mg/dL ↑ | 3.0 mg/dL ↓ | 8.4 mg/dL | 9.2 mg/dL | 408.1 pg/mL ↑ | 85.56 ↑ |
| Risk factor | After reviewing many case reports, case series, and observational studies, the following were observed |
|---|---|
| Age | CUA is more reported in patients in the fifth decade of life. |
| Sex | CUA is seen more in women 2:1 men [4]. |
| Race | CUA affected more whites compared to non-whites [4]. |
| Calcium-phosphorus metabolism | CUA is related to impaired calcium-phosphorus metabolism in dialysis patients as calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, PTH levels and treatment used as vitamin D [7, 8]. |
| Comorbidities | CUA was observed with the presence of other medical diseases (DM-2, obesity, autoimmune conditions, hypercoagulable conditions, and liver disease) [4, 5, 9-11]. |
| Medications | CUA was observed with the use of calcium supplements, calcium-based phosphate binders, active vitamin D, warfarin, corticosteroids, iron therapy, and trauma related to subcutaneous insulin or heparin injections have been associated with increased calciphylaxis risk [12]. |