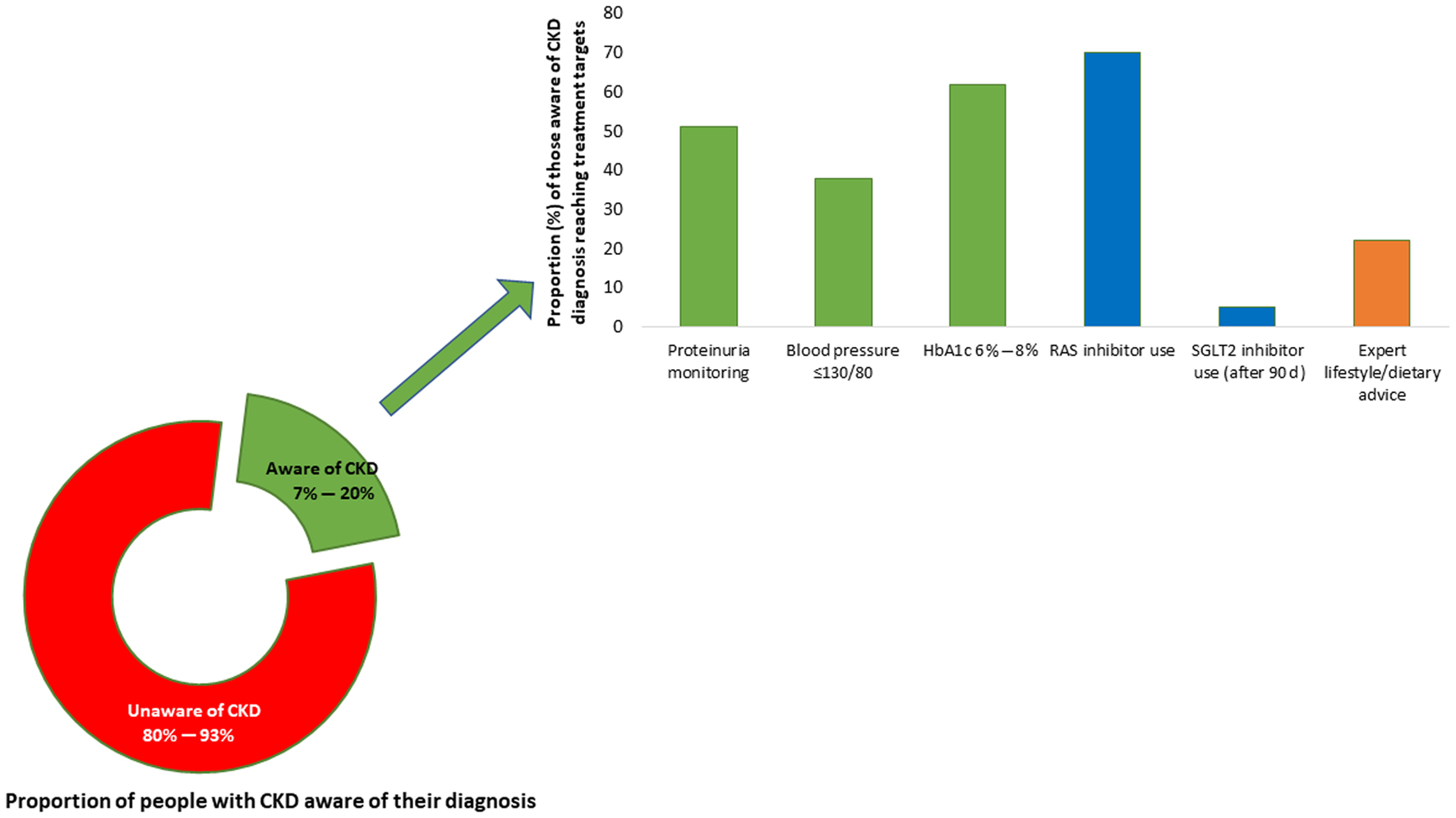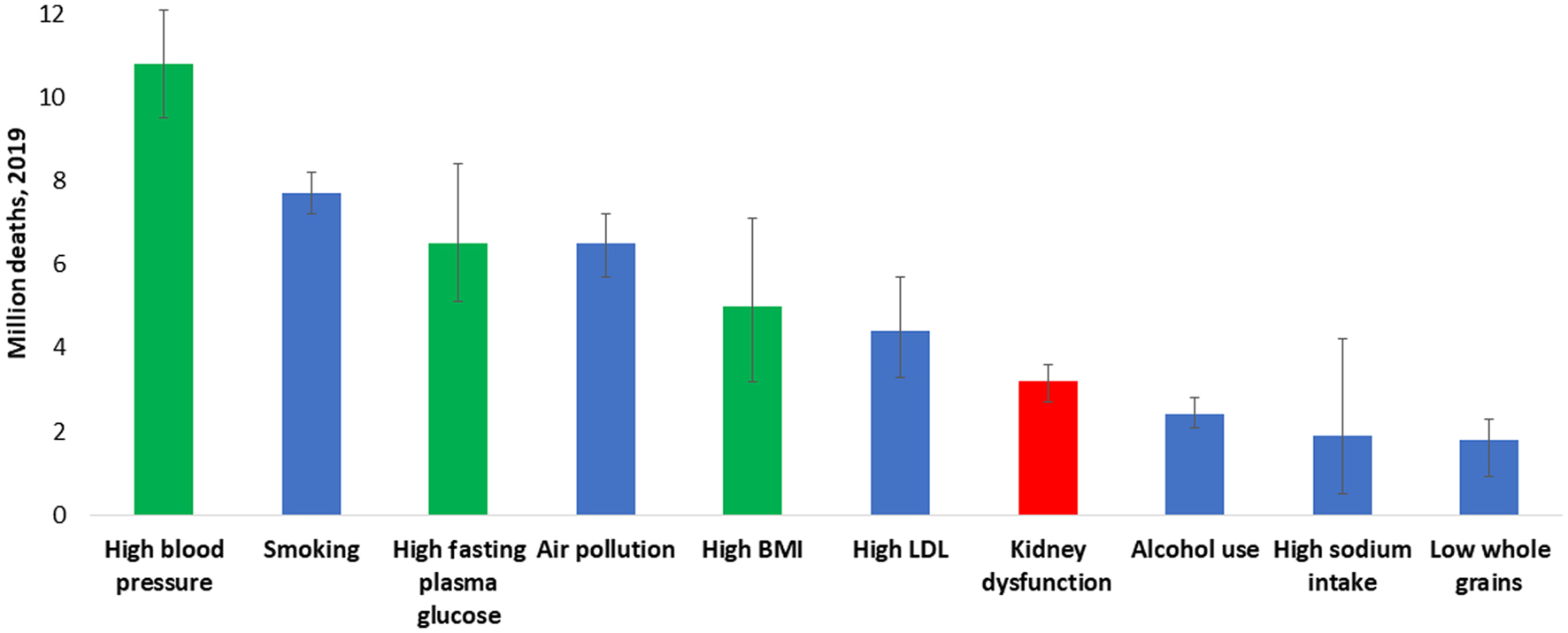
Figure 1. All ages, top 10 global risk factors for death, 2019. Kidney dysfunction (defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or albumin-to-creatinine ratio ≥ 30 mg/g) was the seventh leading global level 3 risk factor for death in 2019. The three leading global risk factors for kidney disease, including hypertension, diabetes, and overweight/obesity, are also leading global risk factors for death; therefore, holistic strategies are required to address all risk factors simultaneously. Ranking is depicted by millions if deaths are attributed to the risk factors. Error bars depict the confidence range. Global ranking of kidney dysfunction stratified by World Bank income category and gender is shown in Supplementary Material 1 (www.wjnu.org). Data obtained from the Global Burden of Disease Study [2]. BMI: body mass index; LDL: low-density lipoprotein.